Goals for this unit:
1. Understand essential theoretical concepts of movement of a particle under a centrifugal force.
2. Know differences between "preparative" and "analytical" types of centrifugation.
3. Analytical Centrifugation
Instrument
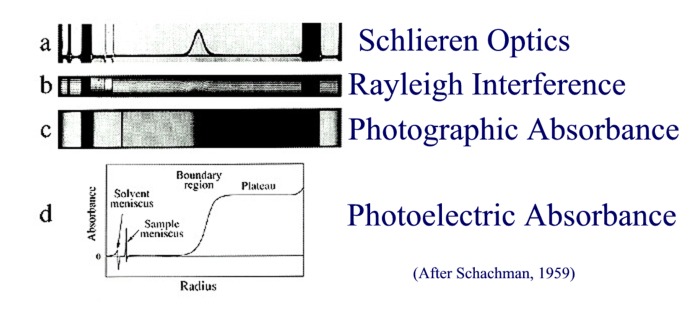
Optic systems - general principles / how to interpret them
Schlieren / Interference / Absorption optics
Common Applications (transport vs. equilibrium experiments)
Sedimentation Coefficient - "s" vs. "S"
Diffusion Coefficient
Frictional Coefficient / frictional coefficient ratio
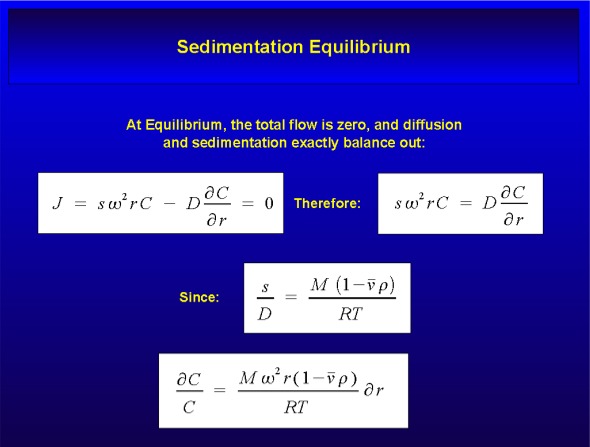
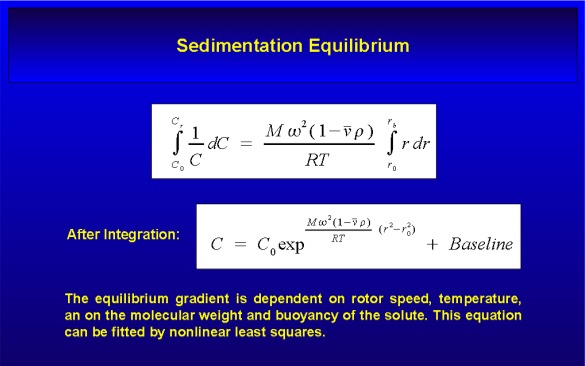
Sedimentation Equilibrium
Our coverage of centrifugation will deal with the following topics, each of which is covered by the web tutorials indicated below. A summary of key equations and topics is given here. Refer to the web sites for further information.
I. Theory - General Principles: (lecture slides)

II. Preparative Methods:
Rotors - Course separations
Density Gradient Methods
Zonal Centrifugation - Sucrose gradient - Rate Method
Isopycnic Methods - Equilibrium Method - Sep. by density (CsCl gradients)
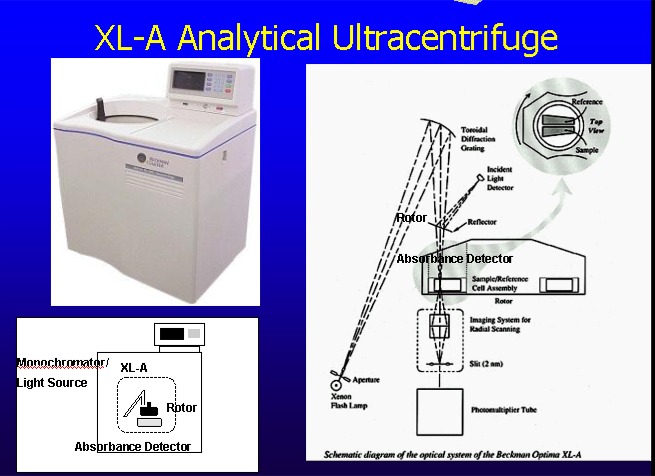
III. The Modern Analytical Ultracentrifuge
See Beckman Review: for a complete discussion of ultracentrifugation (Note pages 15-33).
Comparison of Optic Methods
IV. Analytical Methods
Sedimentation Velocity Experiments -
PDF file on Sedimentation Velocity Methods from Beckman Instruments
The following slides are part of a tutorial on analytical ultracentrifugation Workshop slides.
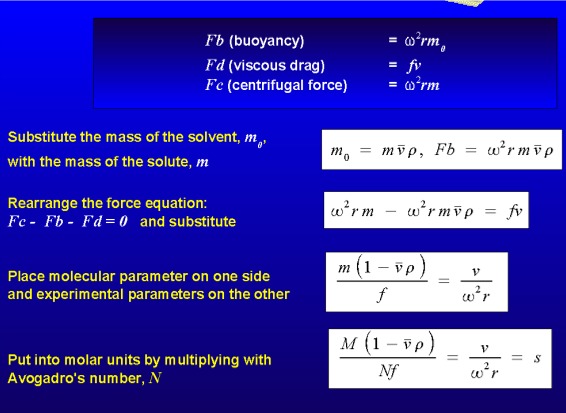
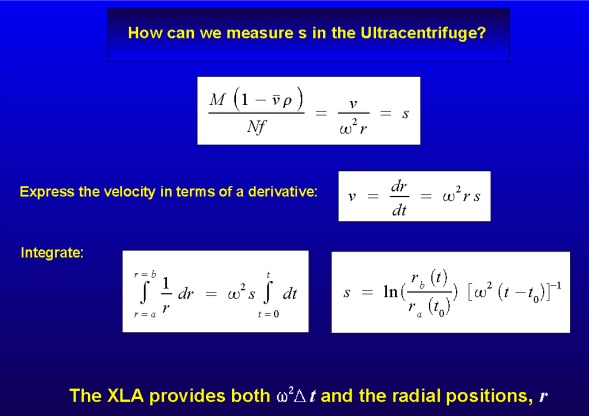
Sedimentation
Equilibrium Methods -
PDF file on Sedimentation Equilibrium Methods from Beckman Instruments