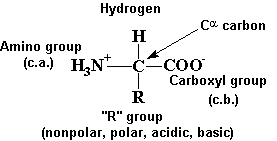Amino Acids and Peptides
-
R - 20 common groups
-
pKa of the COOH group is ~2-2.5
-
pKa of the NH2 group is ~9-10
-
amphoteric-both acid and base character
-
at pH 7, internal salts = zwitterions
-
R groups give each amino acid its unique properties (acidic, basic, hydrophobic,
hydrophilic, etc.)
|
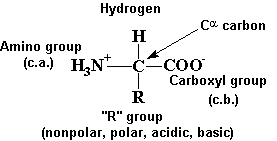 |
Amino Acid Structure
-
a-carbon has normally has 4 different groups attached (except
glycine, R = H)
-
when a-carbon is asymmetric or chiral,
D-isomers or L-isomers
-
amino acids in proteins are in the L form
The
common R-groups -
the “alphabet of life”
(GAVLIPFWYMCSTHKRDENQ)
-
Polarity:
Nonpolar (aliphatic, aromatic);
Neutral - polar;
Acidic;
Basic
-
R =
Hydrogen (
Gly )
Aliphatic
( Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Pro)
Aromatic
( Phe, Trp, Tyr)
Sulfur Containing
( Met,
Cys )
Alcohol Containing
( Ser, Thr )
Basic R Groups
( His, Lys, Arg )
Acidic R Groups
( Asp, Glu )
Amides
( Asn, Gln )
(You should know all amino acids by their 1 and 3 letter
codes.)
Aliphatic or Alkane (Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Pro)
Aromatic Amino Acids (Phe, Trp,
Tyr)
-
Absorb light at 280 nm,
UV absorption used as a measure of protein concentration--Warburg-Christian
-
Tyr side chain has pKa = 10.1
-
The OH of Tyr can also be phosphorylated--regulation of enzyme activity
Sulfur containing amino acids (Met, Cys)
-
Met is (almost always) first amino acid translated (AUG
codon=Met)
-
Cys side chain, pKa= 8.3, carries a net negative charge at
basic pH
-
Cys can form covalent disulfide bond by oxidation ( -C-S-S-C-
)
Hydroxyl containing amino acids (Ser,
Thr)
-
OH group can be phosphorylated, mechanism for regulation
of activity
-
OH group (Ser, Thr) site for attachment of carbohydrates
Basic Amino Acids (Lys, Arg, His)
-
Lys: pKa= ~10; Arg: pKa=
~12; positive charge at physiological pH
-
His is the least basic, pKa= ~6-7; catalysis involving proton transfer
Acidic Amino Acids and Their Amides (Asp, Glu, Asn, Gln)
-
Glu, Asp: pKa= ~4 for acidic side chains--negative charge at neutral pH
-
Asn, Gln; amides forms of Asp, Glu;
uncharged but polar and hydrophilic
Ionization
/ Titration properties of amino acids ;
pKa ‘s
~10
~2
+H3N -
CHR - COOH
R acidic (Glu, Asp )
~ 4
R basic (His ~ 6; Lys ~ 10; Arg ~ 12)
R other (Cys ~ 8 ; Tyr ~ 10)
pH
at which there is no net charge, electrically neutral
amino
acids with ionizable carboxyl side chains (+1
0 -1 -2)
pI= average of pKa’s of the two carboxyl groups ( pI = (pK1
+ pK2) / 2 )
amino
acids with N containing ionizable groups (+2
+1 0 -1)
pI = average of pKa’s of the N groups ( pI = (pK2 + pK3)
/ 2 )
(Another site for viewing AMINO ACIDS
at OMM (Online Macromolecular Museum)
Peptide
Bonds - Proteins are linear polymers of a.a. residues
linked by “peptide bonds.”
-
Reaction:
a.a.R1 +
a.a.R2 =
dipeptide (R1-R2) +
water
DG of this reaction is +10
kJ/mol ; proteins are
metastable
(acid hydrolysis (6N HCl) / proteases
-
Resonance
structures result in planar amide group - trans form is favored
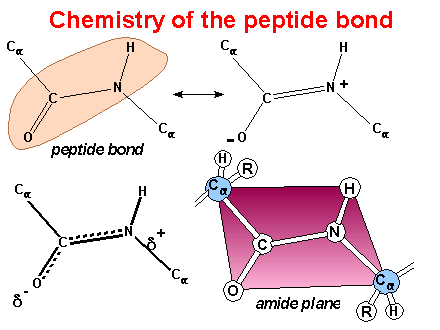
This image
was created by Dr. George Helmkamp, Jr. (UKMC)
-
Peptides
(dipeptide, tripeptide, etc. .....
polypeptide -
proteins)
-
Primary
Structure : +H3N - GVLAADEMLLKFYEE - COO-
N-terminus
C-terminus
-
Animo
acids --> amino acid residues (Glycyl-valyl-leucyl-alanyl-alanyl-aspartyl-
etc.)
-
Blocking
groups: N-terminus (formyl- ,
acetyl- ); C-terminus (amide)
-
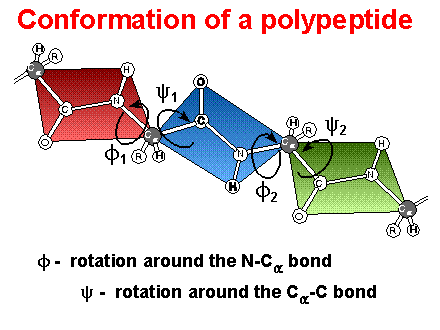
Conformation
of polypeptides -
rotational freedom limited to bonds on a-carbon
-
f is the rotation with N1 bond
-
j is the rotation with the C2 bond
Properties of polypeptides
-
polyampholytes, amino acid side chains determines pI
-
charge on polypeptide varies with pH
-
charge characteristics used for separation of peptides by electrophoresis
- isoelectric focusing in a pH gradient used to determine pI for a protein
experimentally