X-Ray
Crystallography
1. Image Formation
Resolution /
Wavelength (Amplitude, Phase) /
Light Microscopy / EM / X-ray / NMR
2. X-Ray Crystallography
a)
Batch /
Hanging Drop / Standing Drop / Dialysis
b)
Crystal Lattices - Lattice Constants / Space Groups
Role of
symmetry
c) X-ray Sources
Sealed Tube / Rotation Anode / Synchrotron
Relative
flux / advantages of tunable sources
d)Theory
of Diffraction Braggs Law / Reciprocal Space
Bragg
Equation - nλ= 2 d sin(θ)
Real Space
Lattice/cell vs.
Reciprocal Space Lattice / cell
e) Data Collection
Methods / Detectors / Structure Factors
Observed SF
from Intensities: F(hkl)
= SQRT [cI(hkl)]
Calculated
Structure Factors
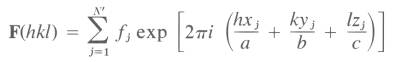
f) Structure Solution
Phase Problem: MIR / MR / MAD
Electron
Density and Structure Factors
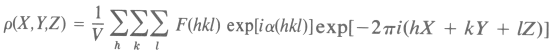
(MIR) = Multiple
Isomorphous Replacement
(Heavy Atom Method)
(MR) = Molecular
Replacement ( Rotation and Translation of Model
Structure)
(MAD) = Multi-Wavelength
Anomolous Dispersion Methods absorption edge
h) Refinements and
Models
Least-squares
+ Energy Refinement (restraints)
i)
Analysis and presentation of results
Visualization programs (Cn3D / RasMol / SwissPDBV / etc)
SCOP Structural Classification of Proteins
CATH Classification / Arch / Topology